What is Phishing?
Phishing is a social engineering technique that tricks victims into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that may cause harm to a device or network system. Phishing is considered the most common cyber-attack vector among organisations today, which often results in reputational, financial or information loss.
Commonly associated techniques often presented in a phishing attack include:
Impersonation
- It is a deceptive technique whereby attackers use a fake identity or mimic a known brand or company to convince victims.
Web spoofing
- A technique that uses website pages that mimic legitimate websites to trick victims. Typically, the elements present from these pages include a look-alike domain, copying the legitimate brand logos to enhance the page’s look.
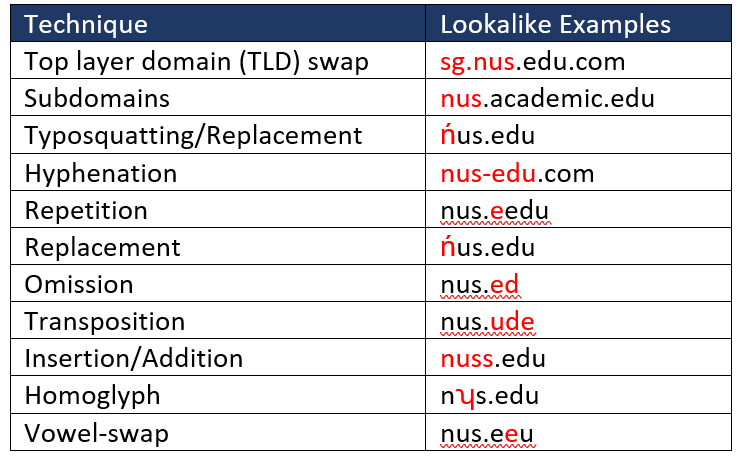
Setting up look-alike domains is a sophisticated technique that convinces victims to think they are still accessing legitimate or related pages.
Some of the methods used to introduce a look-alike domain include the following examples:
Malware
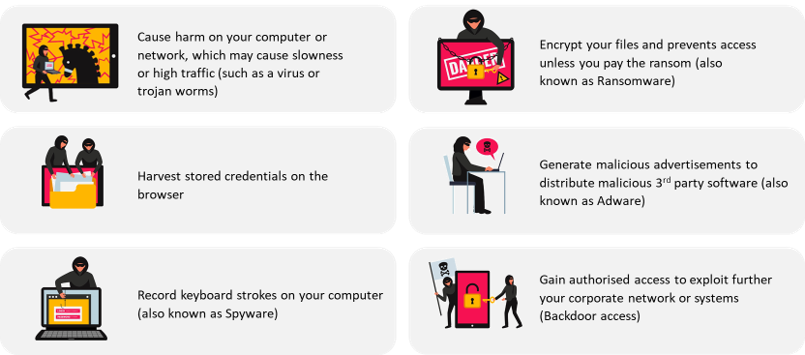
Malware or Malicious Software is often used to complement phishing attacks presented as attachments on emails or links embedded within attachments that directs you to download the malware. A malware, when installed on a machine, may perform different activities that benefit the attacker, such as:
Some of the common formats of malicious software include:
- *.HTM/*.HTML – hyper markup language
- *.JS – Java Script
- *.EXE – Executable
- *.VBS – Visual Basic Script
| IMPORTANT: In some cases, office extensions may also be exploited and embed malicious software codes. However, our Trend Micro solution on email gateways (ApexOne) and end-point agent (Office Scan) performs malware detection and prevents it from getting delivered to your Outlook inbox. |
Other Important Information

