STUDY OF ADSORPTION OF IMIDAZOLE ON IRON SURFACE USING VASP
VASP is a suite of programs that mainly performs density functional theory based calculations (functional such as PBE, LSDA). It uses plane wave as basis to solve the Schrodinger equation, thus it is especially suited for problems which have periodic boundary condition. VASP provides high quality pseudo-potential, which replaces the core electrons of the atoms that are being considered, for virtually all elements in the periodic table. This allows users to obtain accurate DFT calculations at a low computational cost. Our study is to explore, at molecular level, the adsorption of imidazole on iron surface and how the adsorption is relevant to its corrosion inhibiting properties.
When we first study the adsorption of imidazole on iron surface, the main obstacle to perform a VASP calculation is the generation of the coordinate file (POSCAR). It is found that the free program VESTA can do this easily. It can read the crystallography file and generates the required slabs. Subsequent modification can be done using Gaussview. The procedure is outlined in Figure 1.

Next, ionic relaxation or geometry optimization was performed on the POSCAR (VASP input file which contains coordinate, lattice vectors and lattice constant). The ionic relaxation is generally first performed with a conjugate gradient algorithm to determine a step size, which in turn is used in the subsequent quasi Newton algorithm. The converged result for two conformation of imidazoles on Fe(100) is shown in Figure 2.
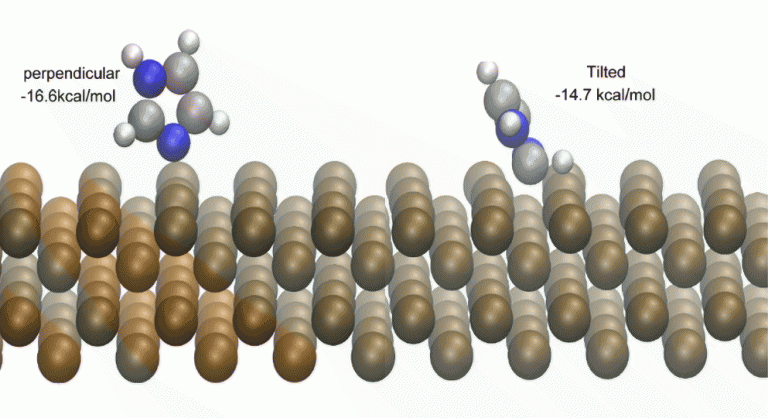
Compared with programs that are based on Gaussian basis set, there is no analytical function for the calculations of vibrational frequency in VASP. Hence, a numerical approach is required if the vibration frequency calculation is required. This can be highly time-consuming. The frequency analysis allows the user to characterize the stationary point based on the number of imaginary frequency. However, VASP has a multitude of molecular dynamic (MD) feature. The basis MD allows one to determine if a structure is correspond to a transition state from its lifetime (transition state typically has a lifetime in the order of femtosecond1, Houk and co-worker has suggested a lifetime of 60fs2). In Figure 3, the tilted conformation in Figure 2 is shown to correspond to an N-H dissociation transition state through MD.
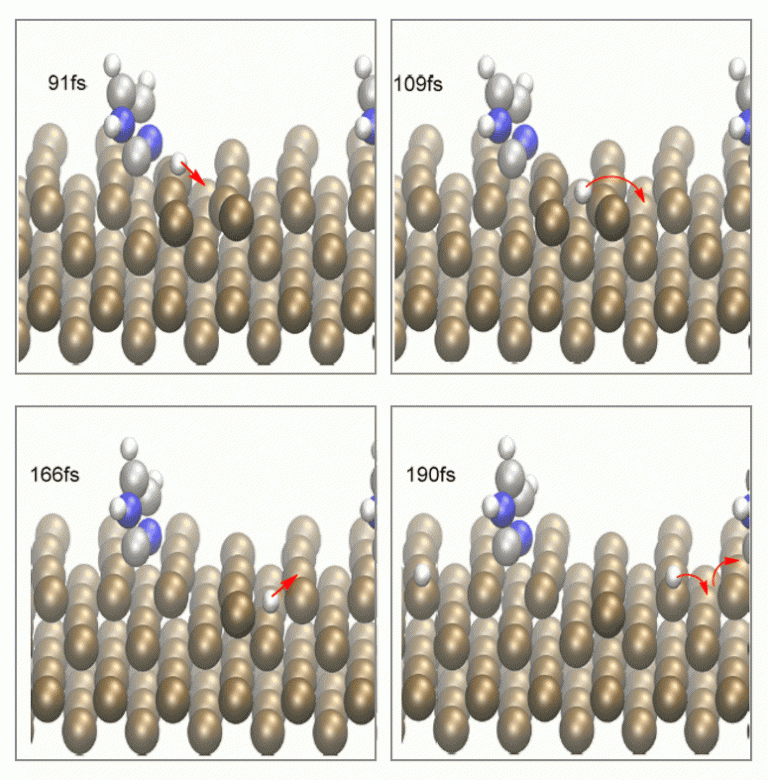
Visualization of VASP output file can be performed with programs such as Visual Molecular Dynamics (VMD), VESTA or xcrysden. Both Figure 2 and Figure 3 are generated using VMD.
We have carried out a simulation using VASP to study the adsorption of imidazole on Fe(100) surface. Ionic relaxations are performed to calculate the binding energy of imidazole adsorption and molecular dynamics to study the time dependent changes. It is believed that the corrosion inhibition properties is due to the formation of a film of imidazole molecules3. We are currently performing further studies to validate this hypothesis.

