2014 REVIEW – DATA, DATA AND MORE DATA
Over the past years, more focus has been placed on data centric development in research computing and HPC, both locally and around the World. We will look at some of the related trends and explore what we need do to get ourselves prepared for the future.
Developments around us
In the US, the NSF (National Science Foundation) recently announced the CORAL project to develop 100+ petaflops HPC cluster systems (the current most powerful HPC system, Tianhe-2, is rated at around 34 petaflops) by 2017 to support extreme scale simulations. The data centric features to be delivered will include an Infiniband interconnection with a bandwidth of 184Gbps. In comparison, the fastest we have on our system is the 40Gbps Infiniband network, more than 512GB of memory per cluster node and a parallel file system with 120PB capacity.
Over in Europe, the Swiss National Supercomputing Centre is offering a 100Gbps network connection to its resources for Switzerland’s scientific community.
Nearer to home, Singapore has recently launched the 100Gbps capable SinGAREN-Lightwave Internet Exchange (SLIX) network connecting research and education institutions such as A*Star, NUS and NTU.
Such data centric HPC clusters, high-capacity storage and fast network systems are required to drive research innovation through large-scale simulations and data processing. For example, the US space agency NASA demonstrated recently an impressive visualization of a year-long changes in carbon dioxide (CO2) level around the globe. The results displayed were part of the simulation that took 75 days to complete and generated nearly four petabytes of data, an extremely data intensive research. Check out this site if you like to know more about the project.
Development at NUS
To enable effective support of data-intensive research, the full data life-cycle as depicted in the figure below will have to be considered.
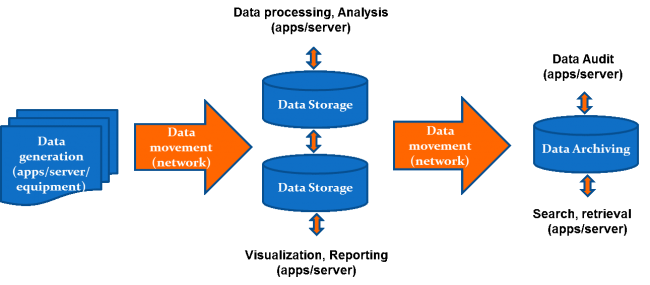
Here are some of the data-centric efforts initiated by Computer Centre to cater for certain requirements within the data life-cycle:
- If data is to be generated at one location (i.e. research lab) and be processed at another location (i.e. Computer Centre data centre), the campus network with multiple 10Gbps links can be used for data transfer.
- More servers and storage systems at Computer Centre data centre are interconnected through 10Gbps network, enabling faster data processing and file transfer.
- More storage space has been added to HPC home folder to support more user applications.
- Cost-effective storage service such as the Utility Storage Service has been introduced to enable large-scale data backup.
- Data management software such as iRODS has been explored to enable data archiving and sharing.
Moving Forward
The following data centric projects will be considered in the coming year:
- Upgrade the iRODS system to improve the ease of use further.
- Explore fast data transfer protocol such as Gridftp to speedup large-scale data transfer.
- Explore commodity storage for large-scale data processing.
- Enable effective research collaboration through the SLIX research and education network.

