Securing Your Data in The Cloud with Open-Source Software, Cryptomator
By Yeo Eng Hee, Research Computing, NUS Information Technology
 Introduction
Introduction
The use of the Cloud to store data and to run HPC analysis jobs has become more pervasive, and one important question users of Cloud storage should ask is: “How secure is my data in the Cloud?”. While some cloud storage providers give users the assurance that their storage in the Cloud is encrypted, and some even provide encryption services and, key management services. It is always good to have an additional layer of assurance, in the unlikely event that there is a data breach in the cloud service provider’s system. Additionally, Cloud service providers may need to comply with governments’ requests to surrender the data in their data centre.
We explore one such open-source tool for encrypting files and folders in the Cloud: Cryptomator, an open-source encryption tool that allows us to safely store the key to our data in our own computer, instead of in the Cloud.
What is Cryptomator?
Cryptomator is an open-source encryption tool which uses AES-256 encryption protocol to encrypt data on the client computer before the data is synchronized with Cloud services such as DropBox, OneDrive or, Google Drive. The encryption is done on a per-file basis, such that only the difference needs to be synchronized. Per-file encryption is faster, unlike some other encryption tools which bundle all the individual files into a single encrypted container. Thus, Cryptomator is very suitable for encrypting and synchronizing data to the Cloud. And since the encryption is done on your computer, before the data is synchronized, you do not have to worry about revealing your data in transit. Cryptomator can be freely downloaded and installed on different device platforms, such as, Windows, Linux, Mac, iOS and, Android.
Testing out Cryptomator
The instructions for downloading and installing Cryptomator on the supported platforms are found at the Cryptomator documentations page at:
https://docs.cryptomator.org/en/latest/
Cryptomator works with any Cloud storage that is mounted on a client computer. To test Cryptomator, we used a Mac with OneDrive mounted on it.
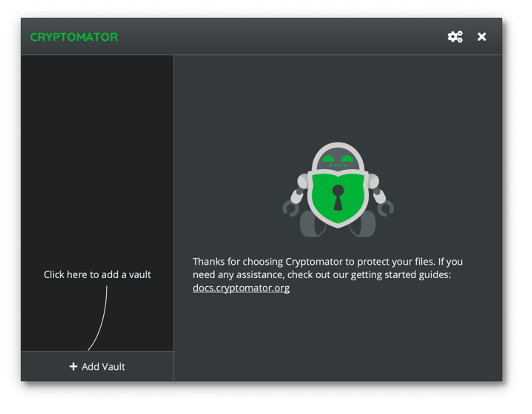 The first step is to create a new vault, using the + Add Vault button as shown in the diagram above. Once we have given the vault a name and specified its location, we have to choose a strong password and click on Create Vault.
The first step is to create a new vault, using the + Add Vault button as shown in the diagram above. Once we have given the vault a name and specified its location, we have to choose a strong password and click on Create Vault.
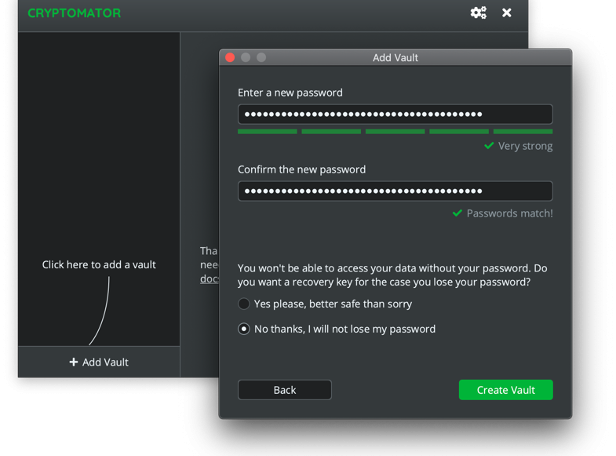 The vault is immediately ready for use.
The vault is immediately ready for use.
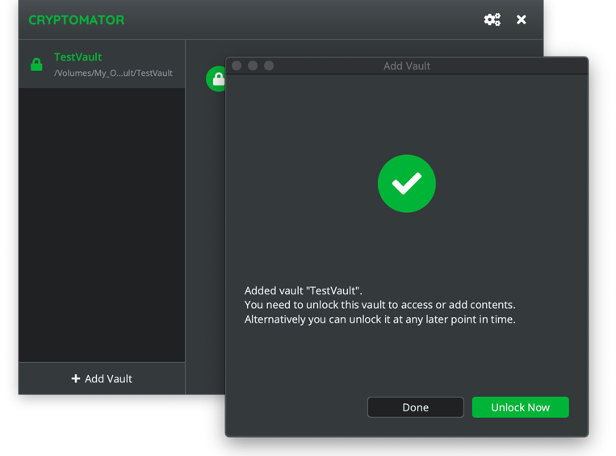 Clicking on Unlock Now, a window pops up for the password to open the vault.
Clicking on Unlock Now, a window pops up for the password to open the vault.
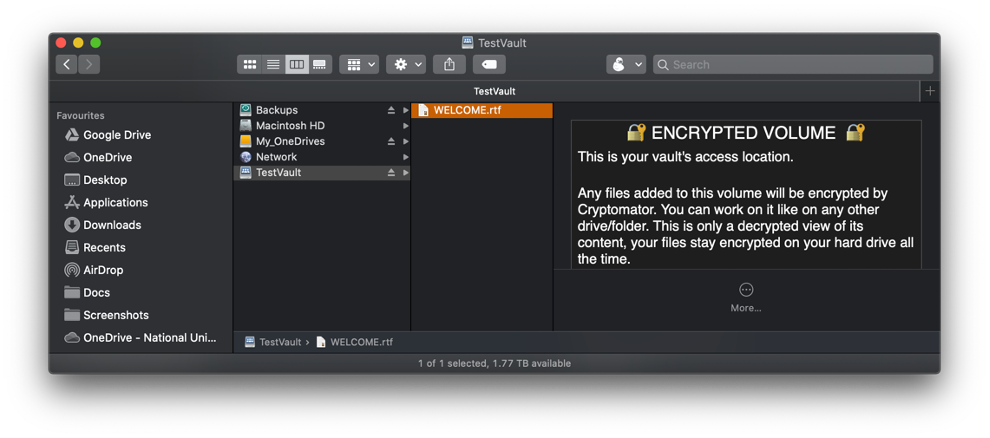
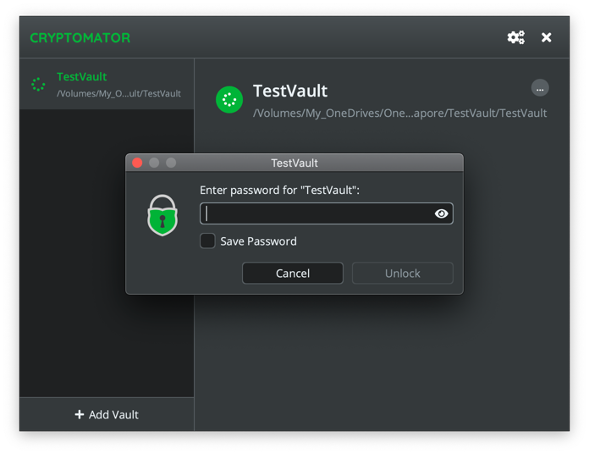 Once unlocked, the vault can be used like any other folder on the client computer.
Once unlocked, the vault can be used like any other folder on the client computer.
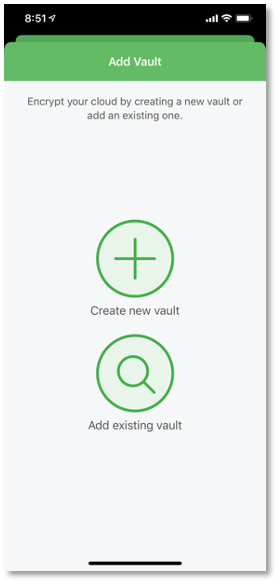
 We could then access the test vault from a mobile device:
We could then access the test vault from a mobile device:
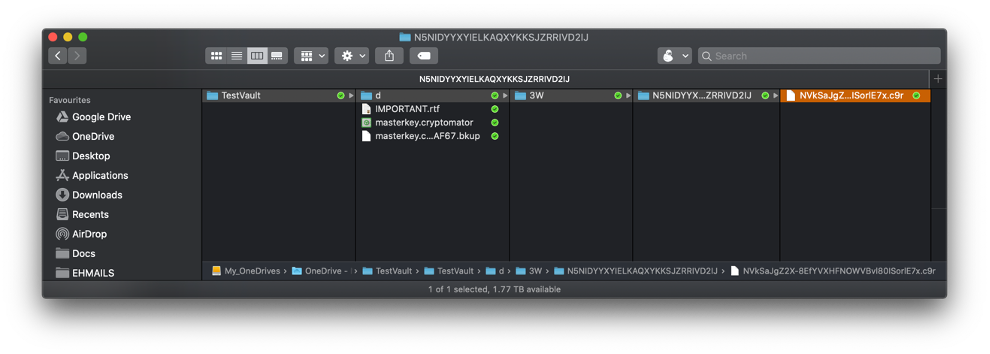
 How does the volume look like when it is locked? The contents will not show any meaningful data as shown:
How does the volume look like when it is locked? The contents will not show any meaningful data as shown:
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Cryptomator is a secure way to encrypt your data in your computer while keeping the security keys in your control, and its file-based encryption makes it suitable for Cloud storage. It uses the standard AES-256 encryption and supports multiple platforms including Windows, Linux, Mac and, even mobile devices such as iOS and Android (note: the mobile apps are not free, even though it is based on open-source desktop version). It is open-source and, therefore, open to audits by independent security researchers (see: Cryptomator.org/faq/ for more details). This tool provides an additional layer of assurance for your data, especially if they are stored in the public Cloud.

